Immediate vs. Delayed Implant Loading
I’d like to introduce you to two patients in my practice. Caroline is a healthy, 23-year-old patient. She has a retained primary lateral incisor at tooth #10 that is decalcified and unesthetic. The tooth has undergone bone replacement and root resorption. As a result, it’s ankylosed but has acceptable bone and adequate facial prominence. An immediate implant and immediate provisional are considered the ideal treatment for replacement.
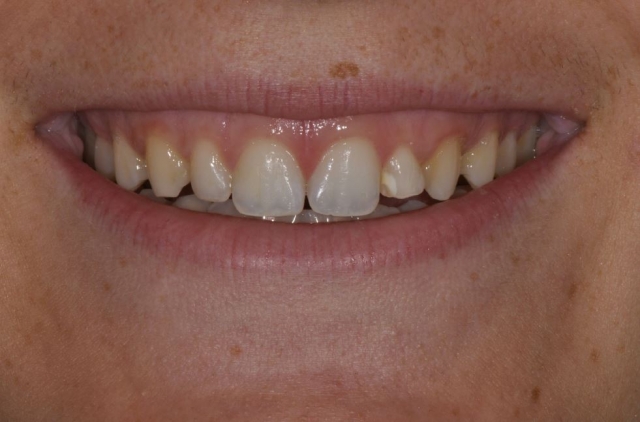
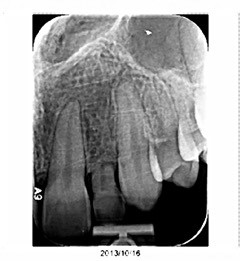
Karen is 64 years old, and her medical history is non-contributory. She, too, requires an implant at tooth #10 because of a tooth fracture from mastication. The existing tooth was deemed non-restorable. There is no periapical infection and a healthy periodontium. An implant was planned as the replacement treatment.
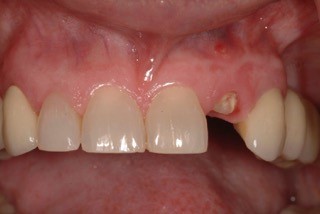
Both Caroline’s and Karen’s lateral incisors were removed, and immediate implants were placed. Although the implant surgeons were different, they were both long-time members of my interdisciplinary team and had significant implant placement experience. Both implants were torqued to 50 Ncm at the time of placement. Provisionals were then placed by me that same day.
The implants were not in occlusion, and instructions for mastication and maintenance were provided. Neither patient wore occlusal appliances or night guards. However, Caroline routinely wore Essex retainers, which her orthodontist provided. I had fabricated a new Essex following her implant provisional. Both implants were allowed to heal for four months before final restoration.
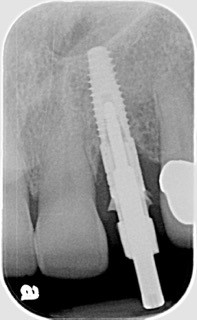
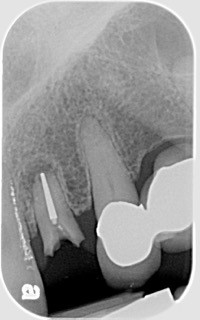
Following four months of healing, Karen was appointed in my office for the final restoration of the implant. The provisional was removed, without anesthesia, and the implant impression post was secured to the newly healed implant. The restorative process was uneventful, and a ceramic restoration and gold post were placed.
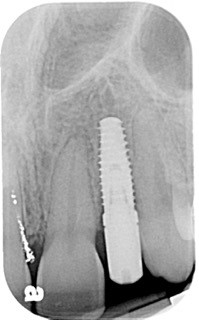
Alternatively, Caroline was scheduled for her implant restorative process. Again, no anesthesia was utilized. The retaining screw was loosened, and the provisional was removed. Upon tightening the impression post to the implant, Caroline winced with pain! The implant was not integrated! Why?
In this scenario, there are two separate implants with perfect indications for immediate extraction, immediate implant placement, and immediate provisionalization, both placed by experienced and competent surgeons. Why does one implant integrate and the other not? These situations are very frustrating for both doctor and patient. Understanding the biology and biomechanics of healing implants may shed some light and provide some guidance for these cases.
Biology of Implants
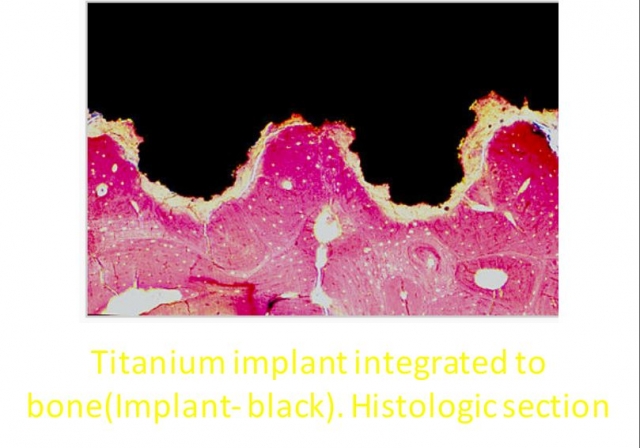
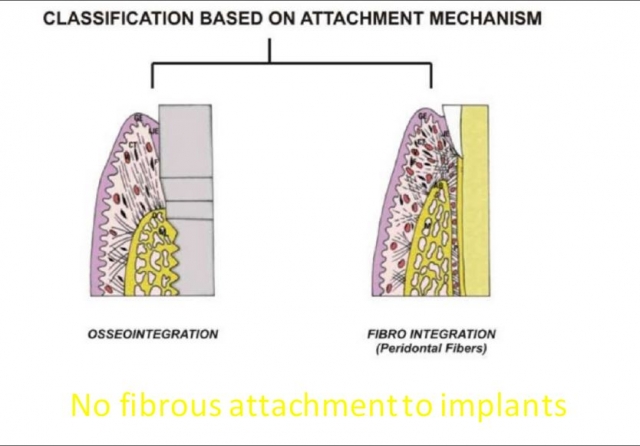
“Osseointegration” is applied to the healed implant/bone interface. It’s “the direct structural and functional connection between ordered bone and the surface of a load-bearing implant.” The two key words in this sentence are “structural” (bone/static) and “functional” (implant/dynamic). These two aspects of integration are key to implant stability and longevity.
The process of placing implants involves the cutting and drilling of the bone. Adequate cooling from water spray and proper speed of osteotomy are essential for reducing the trauma to the cells. The goal is to create intimate contact between the implant and the bony walls of the osteotomy.
This intimacy is referred to as the bone-to-implant contact. It is a function of both the implant length and diameter (BIC). This intimate contact provides the primary stability of the implant. Acceptable stability is verified through the torque testing at the time of placement. 50 Ncm or greater torque is considered acceptable for immediate implant loading.
Regardless of the BIC, micro and mini “gaps” exist at the bone/implant interface. These “gaps” fill with blood and ultimately form clots. Ideally, bone will replace these clots through resorption/replacement. The oxidized layer of the titanium implant creates a cellular response that promotes adhesion and cellular proliferation. This is the “structural” component of healing implants. The “static” aspect of primary stability is essential to allow adequate healing to occur before “loading” of the implant.
The “functional” aspect of implant loading relates to the forces applied to the implant. Although the implant is stabilized at the time of placement, functional forces of occlusion and mastication can be detrimental to adequate healing and bone formation. From a biomechanical standpoint, the type and amount of force applied to the healing implant is critical for successful integration. In biomechanical terms, the implant heals through a “bonding” process to the bone.
Osseointegration of Implants
When the implant is fully osseointegrated, it is classified as “bonded.” Bonded implants can accept compression, shearing, and tensile forces. Integrated implants are stable. “Un-bonded, or healing, implants are initially less stable. They can accept the frictional forces of implant placement and provisional fabrication, but not tensile force.
Excessive implant micro-motion interrupts the vascularity that is essential for proper healing. This interruption may lead to collagen fiber formation around the implant rather than the desired osseointegration. Non-axial loading applies significant tensile forces that are detrimental to integration. When we load immediately placed implants through provisionalization, we introduce dynamic forces that can positively and negatively affect implant healing.
We know through studies that tissue response to immediate loading can have favorable results in the peri-implant tissues. But care must be taken to not overload the biologic system with functional force!
We can control the forces and manage the micro-motion. We have several options available to do this. The most obvious is to avoid occlusal contact on newly placed provisionalized implants. As stated earlier, vertical forces are a concern, but lateral force is contraindicated in healing single-tooth implants. Splinting multiple implants provides “group” support in resisting implant motion.
Bone quality is also an important factor to evaluate. Type I and II bone (lower and upper anterior regions, respectively) are denser and provide greater initial stabilization of the implant. Type II and IV bone(posterior regions) are more trabeculated and less dense.
Another factor is implant design and surface texture. Thread design and pitch may increase the area of implant surface for bone contact. The texture of the implant also plays a role. Textured implants increase surface area for bone cell contact better than machined surfaces.
Lastly, implant diameter and length are significant considerations in implant stability. The longer the implant, the greater the surgeon’s ability to engage bone and achieve primary stability, especially in an immediate extraction — immediate placement scenario. Wider implants provide greater BIC for healing, but implant stability and the emergence profiles of the abutment are limitations for a “wider is better” concept. Ultimately, force management is the key to successful implant integration and longevity!
With these biological and biomechanical factors of implant failure to consider, why would we immediately load? What are the benefits of immediate placement/loading? Is delayed placement/loading better?
Which Is More Beneficial: Delayed or Immediate Implant Placement?
One of the most significant factors of immediate placement is that it decreases treatment time. The healing process of implant therapy is definitive. Depending on all the biologic factors discussed previously, osseointegration occurs slowly. Our patients do not always understand this concept and are not as willing to accept this delay. Patient education is a key factor. Immediate loading certainly increases patient acceptance. Immediate placement of implants at the time of tooth removal maintains optimal soft tissue contours and tissue esthetics.
The emergence profile of the tooth root is more easily captured in the immediate provisional contours, thereby supporting the soft tissues ideally. And, in the absence of infection, the bone response(biology) of the immediate placed implant is favorable.
Delayed placement and loading are also considered. By delaying placement, the tooth site infection may be resolved before implant placement. There is a greater percentage of osseointegration in a healed site than infected site. By delaying the implant placement and allowing the soft tissues to heal, there is better soft tissue volume for surgical flap adaptation and implant coverage when placed. Additionally, bone regeneration can occur within the site by allowing the surgical site to heal, and improved initial implant stability would be attained.
There are a couple of downsides to delayed placement and loading. Not only is there an increase in treatment time, but there is the potential of bone and tissue resorption that may occur from this delayed approach. Soft tissue contours are critical for esthetic implant success, especially in the anterior. Loss of tissue contour and loss of supporting bone by delaying treatment, may jeopardize the esthetic results of implant tooth replacement.
Many factors must be considered before deciding upon immediate versus delayed implant placement. The patient’s presentation and implant site conditions must be thoroughly evaluated. But immediate loading should not be indiscriminate!
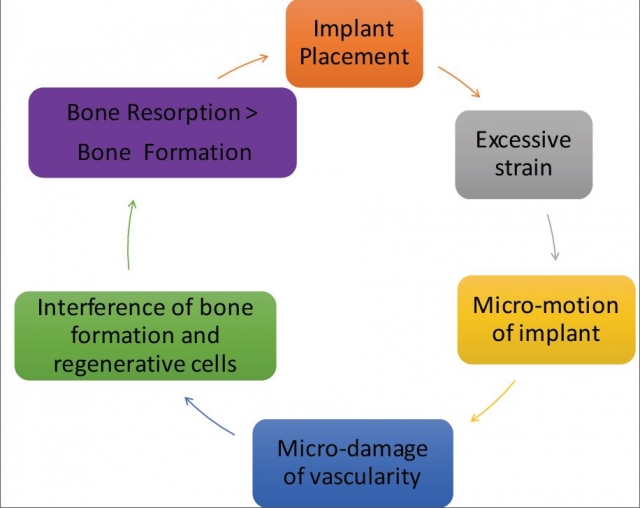
The biologic/biomechanical cycle diagram provides a synopsis of the factors involved in the success or failure of immediately placing and loading implants.
Implant osseointegration is a complex process of biology and biomechanics. Immediate implant loading is successful because of a favorable biologic response to stress. Biomechanical design and control of forces on the implant lead to good outcomes. It’s not safe to indiscriminately load dental implants. A thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical health, dental presentation, and overall objectives will aid in determining implant placement and implant success.
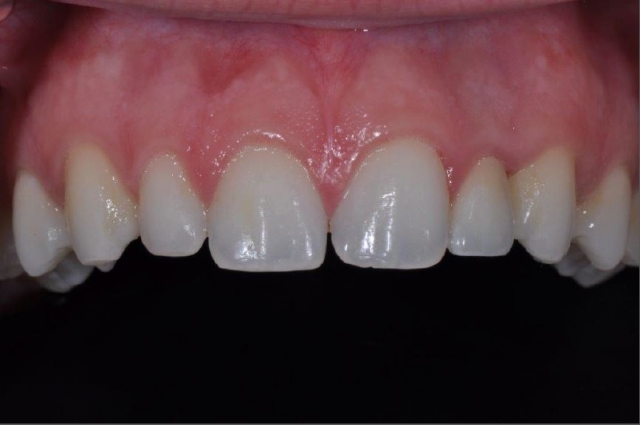
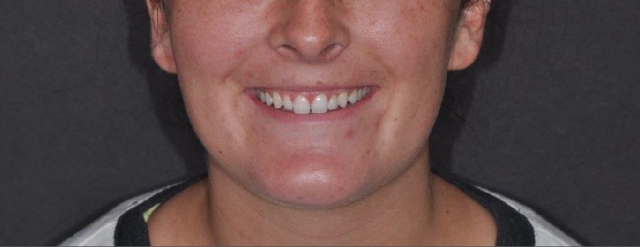
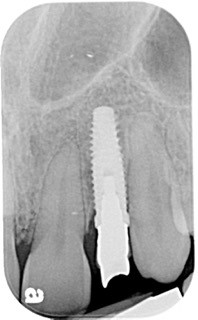
So, the question remains as to why Caroline’s implant failed. She presented with the ideal circumstance for immediate placement and immediate loading of the implant. All precautions were taken to avoid failure, but osseointegration did not occur. Caroline and her parents were as disappointed as I was that implant failure occurred.
But because I could help them understand this biologic and biomechanical process, they were supportive of implant replacement.
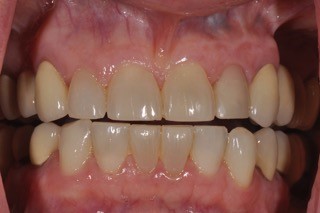
The failed implant was removed. Following the healing of the site, a second implant was placed. Again, a provisional was placed on the new implant at the time of placement. Maintenance and care instructions were provided. This implant healed uneventfully four months before final restoration. Caroline was delighted with this result.
Unfortunately, I do not know why this failure happened. However, by having knowledge and understanding of the implant integration process, we can better communicate with our patients and guide the direction of treatment and its success.
References
- Mayfield, L. J. A. (1999). Immediate, delayed and late submerged and transmucosal implants. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Workshop on Periodontology, Implant Dentistry, 1999 (pp. 520-534). Quintessence.
- Barndt, P., Zhang, H., & Liu, F. (2015). Immediate loading: from biology to biomechanics. Report of the Committee on Research in fixed Prosthodontics of the American Academy of fixed Prosthodontics. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 113(2), 96-107.
- Seriwatanachai, D., Kiattavorncharoen, S., Suriyan, N., Boonsiriseth, K., & Wongsirichat, N. (2015). Reference and techniques used in alveolar bone classification. Journal of Interdisciplinary Medicine and Dental Sciences, 3(2), 172.
- Misch, C. E., & Abbas, H. A. (2008). Contemporary implant dentistry. 3rd. St. Louis: Mosby, 1061.
- Bedrossian, E., Sullivan, R. M., Fortin, Y., Malo, P., & Indresano, T. (2008). Fixed-prosthetic implant restoration of the edentulous maxilla: a systematic pretreatment evaluation method. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 66(1), 112-122.
SPEAR campus
Hands-On Learning in Spear Workshops
With enhanced safety and sterilization measures in place, the Spear Campus is now reopened for hands-on clinical CE workshops. As you consider a trip to Scottsdale, please visit our campus page for more details, including information on instructors, CE curricula and dates that will work for your schedule.

By: Jeffrey Bonk
Date: February 6, 2018
Featured Digest articles
Insights and advice from Spear Faculty and industry experts