Lithium Disilicate Resin-Retained Adhesive Bridgework in Fixed Prosthodontics
In 1503, Leonardo da Vinci said, “Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.” Today, these words are often lost when it comes to the art and science of dentistry. Restorative dentists frequently plan complex, expensive, time-consuming, and high-risk treatments when a simpler solution would achieve the same result.
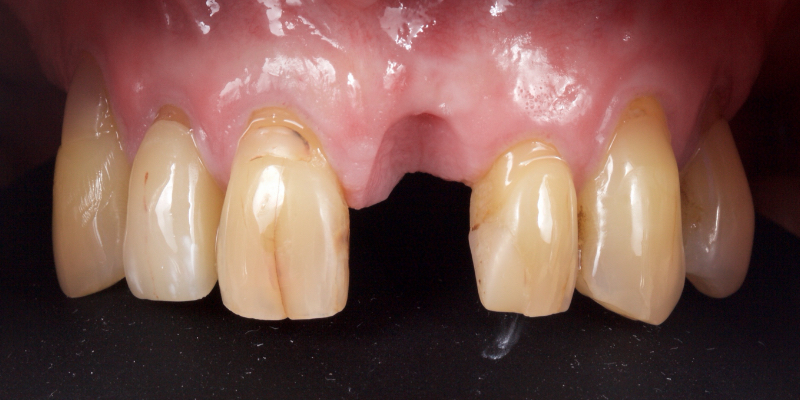
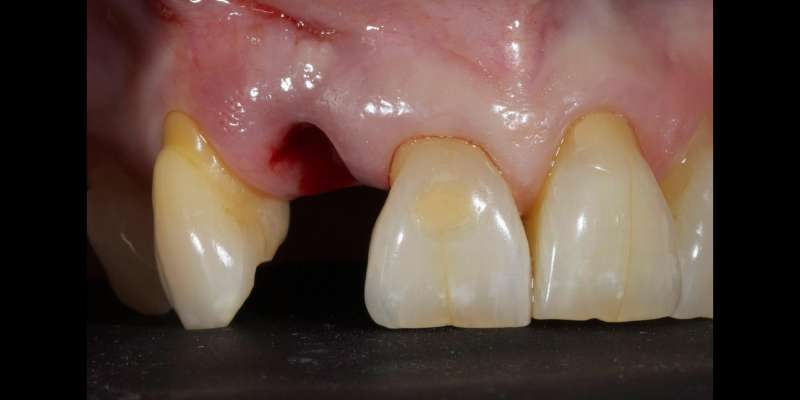
Take Arthur, a 76-year-old man who presented with a vertical root fracture of his upper left central incisor. His medical conditions precluded his request for an implant, so he agreed to the proposal for an adhesive bridge instead.
The tooth was extracted and for four months the pontic site was conditioned with a removable Essix-type of denture (Fig. 1).
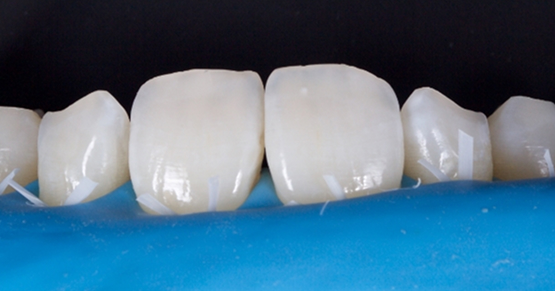
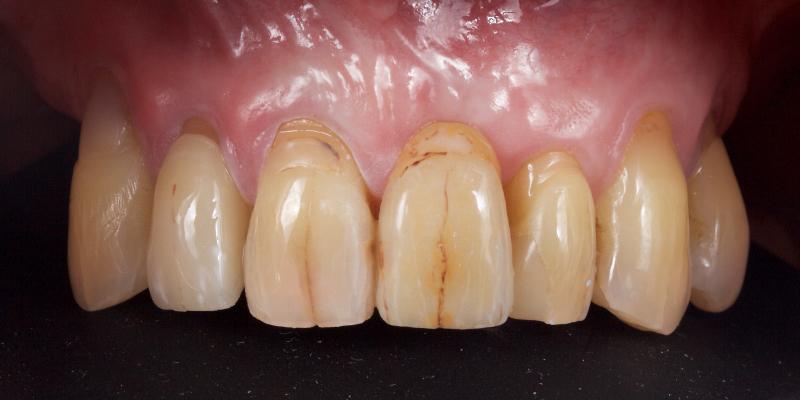
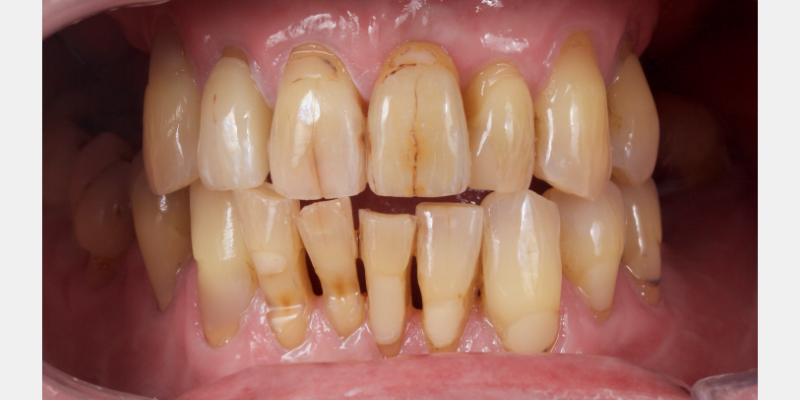
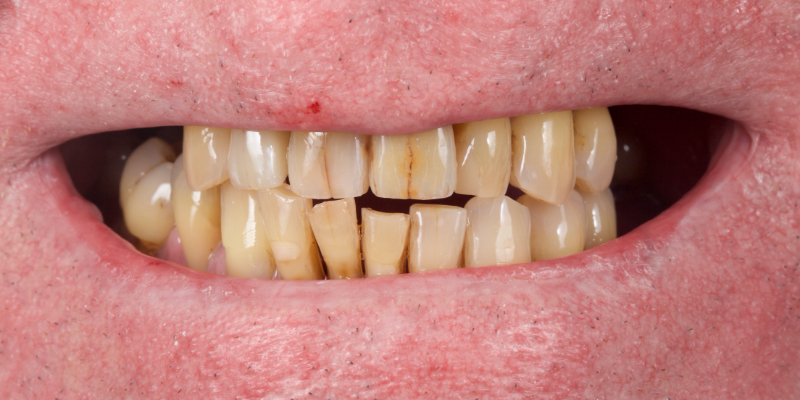
An e.max (lithium disilicate), one-wing (adjacent central being the retainer) bridge was placed, which resulted in an acceptable outcome (Figs. 2-4) that was more timely and at a lower financial and biological cost to the patient than the implant Arthur initially thought he wanted.
Classification of Adhesive Bridgework
Adhesive bridgework may be fabricated directly or indirectly. Direct adhesive bridgework means the work is done chairside during a single appointment. The pontic may be either the natural tooth or a denture tooth, and it can be bonded in situ. Directly fabricating the bridgework provides a simple, inexpensive solution for emergencies (e.g., root fracture or spontaneous loss for periodontal reasons) or if a patient has limited finances.
Jenny is an example of a patient who benefited from direct adhesive bridgework. She presented with a perio-endo lesion not amenable to treatment and she had a limited budget for treatment.
The tooth was extracted (Fig. 5) and the root resected to create a 3.0 mm subgingival ovate pontic.
The pulp was simply extirpated with a bur via an apical approach and the cavity was filled with direct resin (Figs. 6-7).
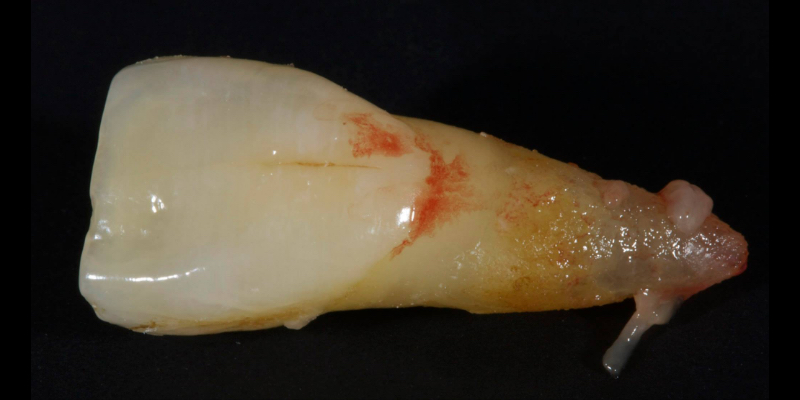
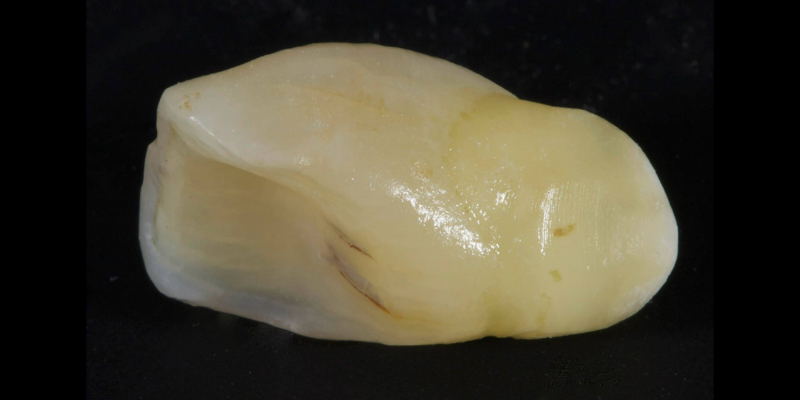
The pontic must retain the same volume as the extracted tooth (i.e., not be narrowed) to guide the post-extraction soft tissue during healing and preserve the papillae. The tooth is then bonded back in situ with a flowable composite and fiber splint, like Ribbond (Figs. 8 and 9).
Adhesive bridgework may also be fabricated indirectly, meaning the prosthesis is made in a laboratory. Indirect adhesive bridgework may be further subdivided into:
- Retention via orthodontic pads (a largely obsolete technique)
- All ceramic (e.g., lithium disilicate or zirconia)
- Cast metal (usually nonprecious) can be classified according to the mechanism of:
- Macromechanical (e.g., Rochette-type design)
- Micromechanical (e.g., Sandblasting)
- Micromechanical and chemical (e.g., silanization of ceramics)
Indications and Criteria for LiDiSi
The classic adhesive bridge design is the etched cast metal variant, which has existed since the 1970s. It’s a highly successful and predictable design; however, it has drawbacks, like metal shining through, which results in greying and loss of value, especially for translucent teeth. Also, there is an increasing problem of metal allergy for some.
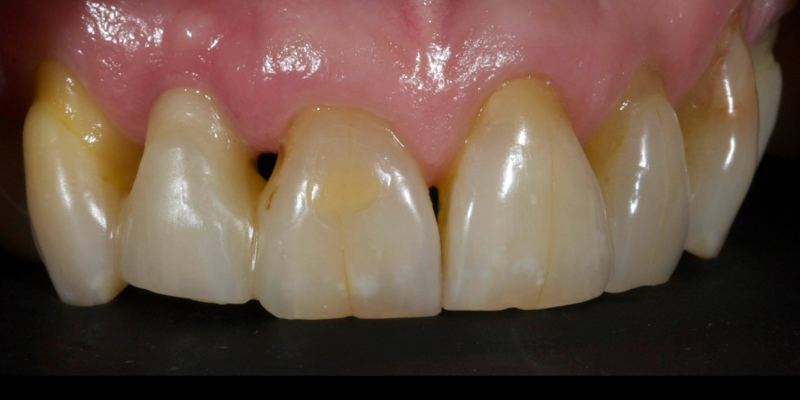
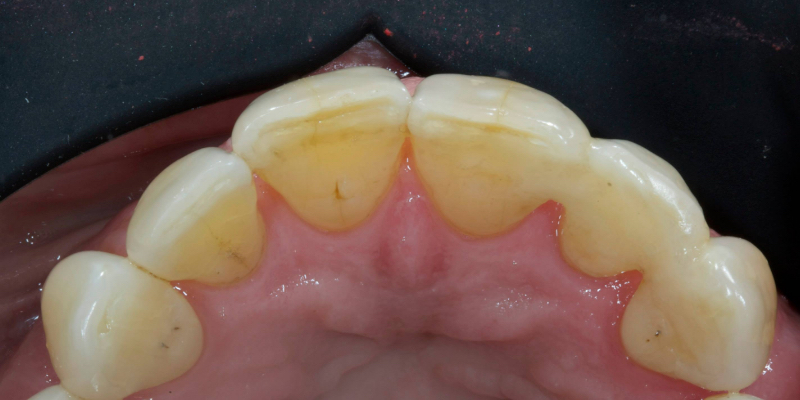
More recent advancements use all-ceramic pontics and retainers, such as lithium disilicate (e.g., e.max, Ivoclar and LiSi, GC) and zirconia. Lithium disilicate (LiDiSi) offers high-quality esthetics, excellent mechanical properties in the anterior zone, and predictable bondability. I’ve been using this material in this application for more than 15 years. Here’s a case on a 17-year recall (Figs. 10 and 11).
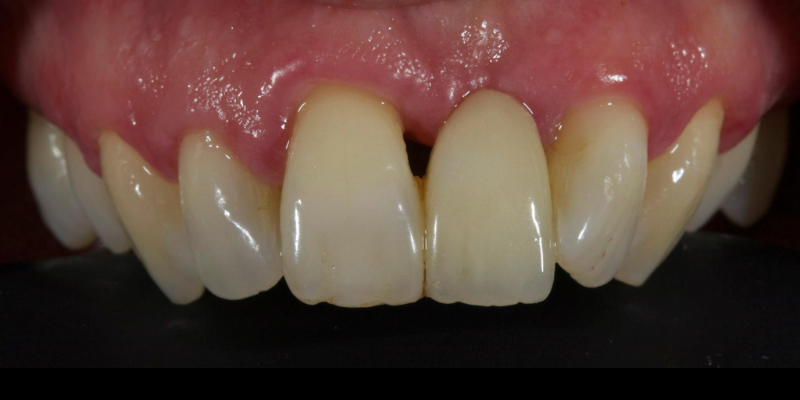
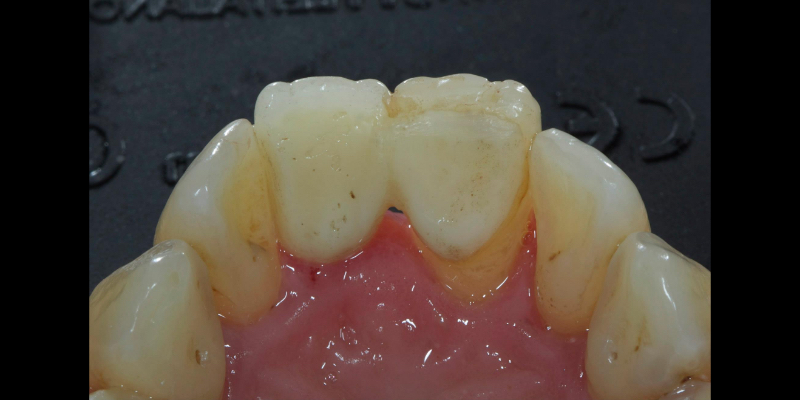
Cases like this are typically completed without preparation other than light particle abrasion of the enamel surface to remove aprismatic enamel and improve bond strengths (29-micron alumina at 2-3 bar is usually sufficient). Occasionally, a deep cingulum pit is blocked out with direct flowable composite before impression.
Preserving enamel results in higher bond strengths. In addition, it maintains the rigidity of the abutment tooth, which means it flexes less in function, increasing the predictability of the final prosthesis.
If existing Class III or palatal cingulum restorations are present, these can be removed and incorporated as resistance features preoperatively. The only reason to consider preparation is for a lack of interocclusal space; however, this can be overcome without preparation, either by:
- Slightly reducing the incisal edge of the opposing tooth; however, attention should be paid to the impact of this approach on the occlusion regarding to protrusion and transition to edge-to-edge.
- Adding composite resin to the palatals of the anterior teeth — the Dahl Approach. Over 6-22 months, the posterior units over-erupt and come into contact. The composite resin can then be removed from the abutment teeth, leaving space for the ceramic wing.
- Gaining space via equilibration in cases that have a high horizontal. Vertical component (Hv) of the slide from CR to MIP space may be gained by occlusal equilibration to CR.
The wing should cover the largest possible surface area for maximum adhesion and retention form. The main factors to consider in the prosthesis design are:
- The pontic mesiodistal width should not exceed 11.0 mm.
- The connector area between pontic and retainer wing should not be less than 16.0 mm; otherwise, there is a potential for fracture due to cohesive failure of the material. This is very simple to estimate preoperatively on a study model or scan by measuring the area of the interproximal surface of the abutment tooth, which is typically triangular; ergo, the area is half base (the buccolingual width gingivally) X height (the gingivo-incisal height) (Fig. 12).
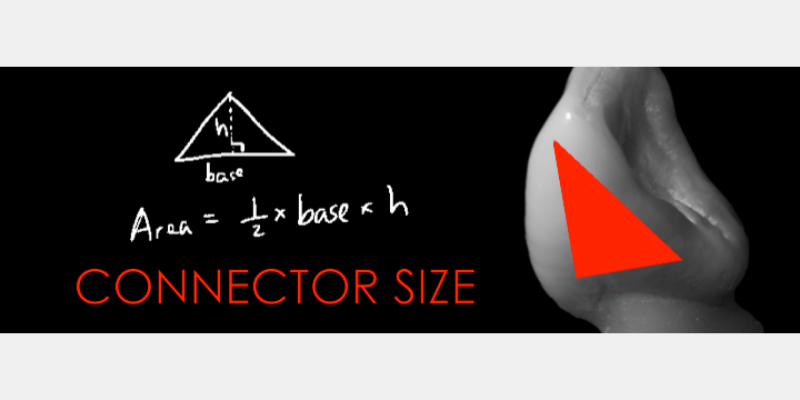
This means the material selection is usually best suited to upper central incisors and canines as abutments, whereas lower anterior teeth are less ideal. Extending the connector size vertically is preferable to the sagittal plane to gain adequate surface area.
- I’ve found pressed ceramic is superior to CAD/CAM since it generally offers better fit (and therefore results in thinner cement lutes) and has superior mechanical properties. The wing and connector should always be pressed without any cutback to maintain mechanical strength. The pontic may be cut back on the facial and layered for esthetics; however, I generally prefer the mechanical strength advantages offered by simple stain and glaze.
- In most cases, a single wing is preferred due to the risk of a single abutment debond and consequent secondary caries with multiple wings.
Provisionalization
Provisionalisation of adhesive bridge cases is challenging since there is no retention/resistance form to retain the prosthesis. Commonly, a removable partial denture is employed; however, this may be unacceptable to the patient. I prefer the precision and stability of a fixed solution if grafting is required or during the development of the saddle area for an ovate pontic.
If a fixed adhesive provisional is employed, a good approach is to use a Rochette-type nonprecious bridge with three holes in the wing. This is retained by simply etching into the holes, rinsing, drying, and placing three separate increments of paste composite.
The composite can be easily removed with a bur and popping off the wing with a sharp curette. It is desirable to use a nonstrategic tooth (i.e., not the tooth that is planned to be the final abutment) as the abutment for the provisional, since minor changes to the palatal contour caused by bonding and removing the provisional may result in a suboptimal fit of the final prosthesis. The pontic is typically fabricated from acrylic or composite because this is more economical and easier to add to and modify when contouring the soft tissue.
Here’s Elizabeth’s case. She had a periodontal lesion affecting the upper right central incisor (Fig. 13).
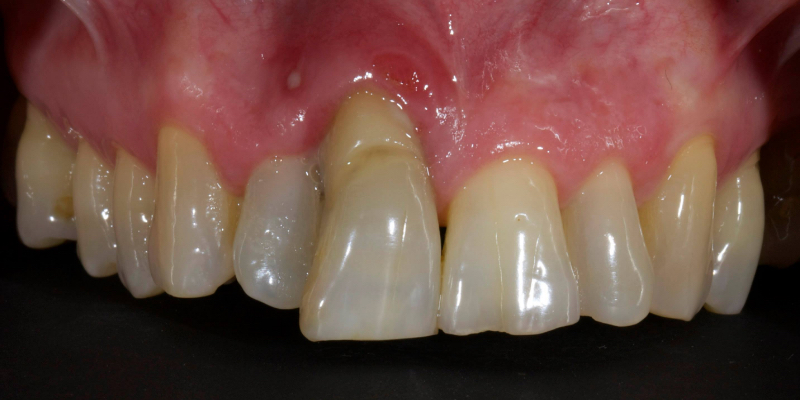
The tooth was extracted and a provisional nonprecious adhesive bridge with composite pontic was placed (Figs. 14-16).
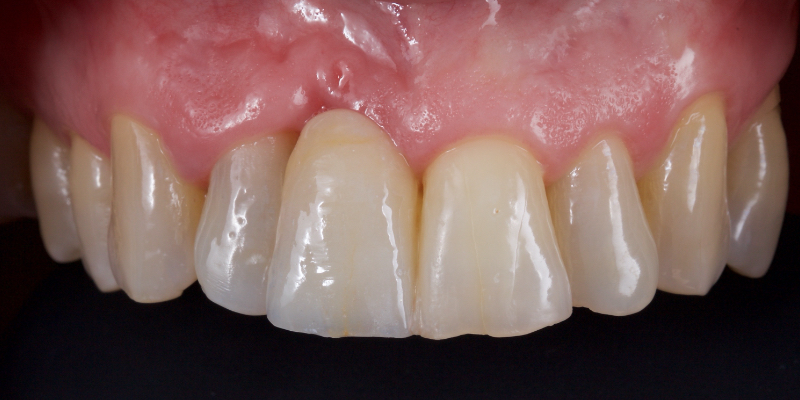
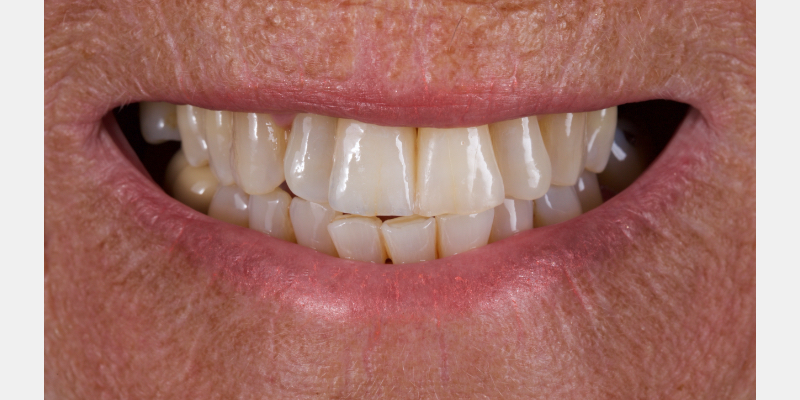
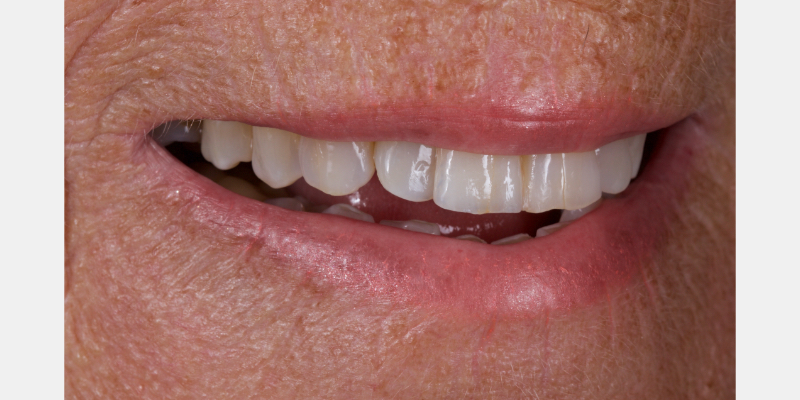
The Rochette-type wing was placed on the lateral incisor abutment (Fig. 17). Grafting procedures were carried out before definitive restoration with a lithium disilicate adhesive bridge.
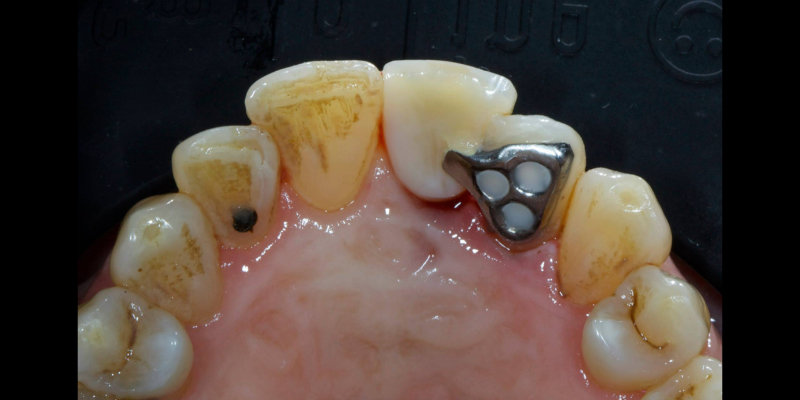
Cementation
Cementation is simple following this sequence:
- The restoration is tried in to verify fit and esthetics
- The wing is etched with hydrofluoric acid for 20 seconds, dried, and silanated.
- The tooth is isolated, etched with 37% phosphoric acid for 30 seconds, and primer/ adhesive applied but not polymerized because the film thickness will affect the fit.
- Heated regular composite resin (45-degrees) is applied to the intaglio of the wing and the prosthesis seated. Clean up is extremely simple with an explorer and Super Floss. Using heated composite means the bridge is more stable during clean up and before polymerization.
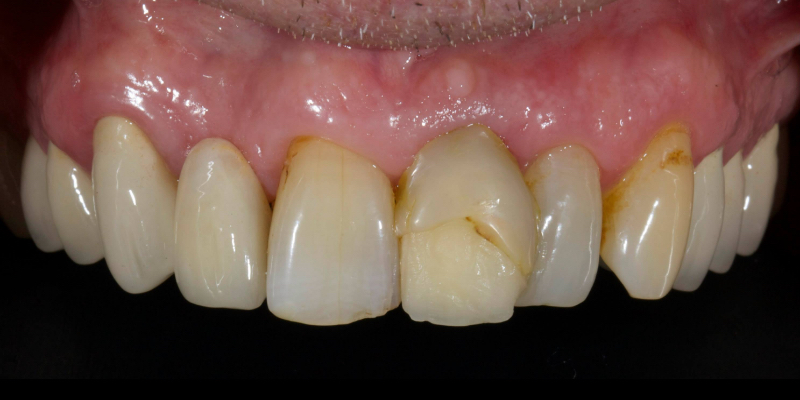
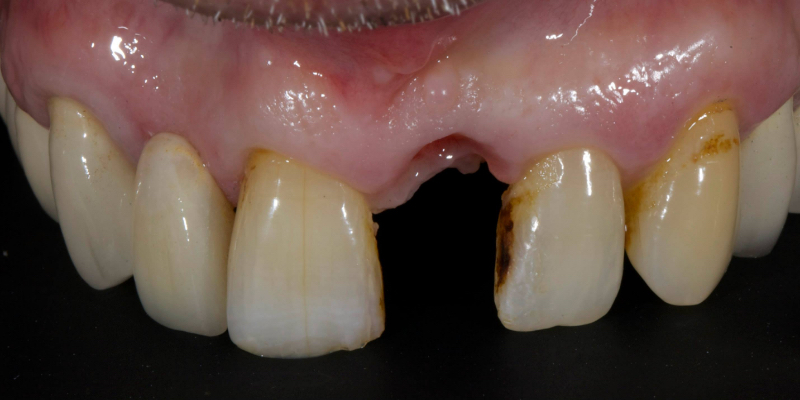
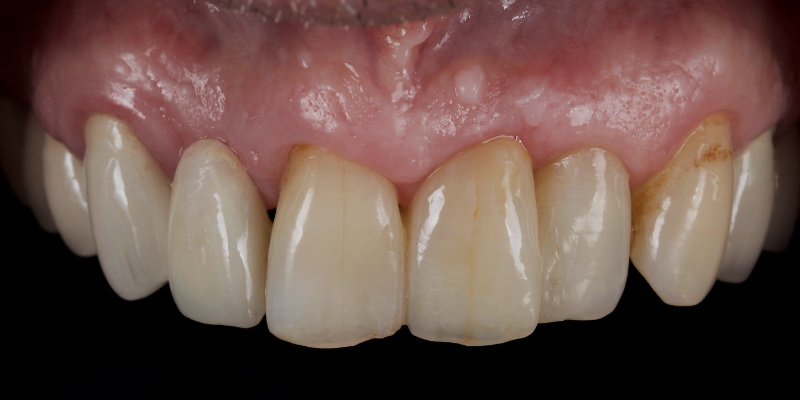
Here’s John’s case bonded with heated resin. He had a failing, older metal, ceramic adhesive bridge (Fig. 18). The bridge was carefully removed (Fig. 19) and the final bridge was seated (Fig. 20).
Research published in 2015 suggested most failures occur in the initial four years with few consequences and the estimated survival rate was 80.4% at 10 years. Failure is commonly a debonding, so it is a simple matter to rebond at minimal financial and biologic cost for the patient.
References
- Da Vinci L. (1503). Studies of Machinery (verso of Studies for the Christ Child with a Lamb)
- Glauser R, Thievent B, Scharer P. (1998). Ovate Pontic: Clinical and Technical Aspects. Teamwork Interdisczipl J Prosth Zahnheilkd, 1: 258-277.
- Spear, F. M. (1999). Maintenance of the interdental papilla following anterior tooth removal. Practical Periodontics and Aesthetic Dentistry: PPAD, 11(1), 21-8.
- Tay, W. M. (1992). Resin-bonded bridges: a practitioner’s guide. (No Title).
- Howe, D. F., & Denehy, G. E. (1977). Anterior fixed partial dentures utilizing the acid-etch technique and a cast metal framework. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 37(1), 28-31.
- Dahl, B. L., Krogstad, O., & Karlsen, K. (1975). An alternative treatment in cases with advanced localized attrition. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 2(3), 209-214.
- King, P. A., Foster, L. V., Yates, R. J., Newcombe, R. G., & Garrett, M. J. (2015). Survival characteristics of 771 resin-retained bridges provided at a UK dental teaching hospital. British dental journal, 218(7), 423-428.
SPEAR ONLINE
Team Training to Empower Every Role
Spear Online encourages team alignment with role-specific CE video lessons and other resources that enable office managers, assistants and everyone in your practice to understand how they contribute to better patient care.

By: Jason Smithson
Date: August 17, 2020
Featured Digest articles
Insights and advice from Spear Faculty and industry experts