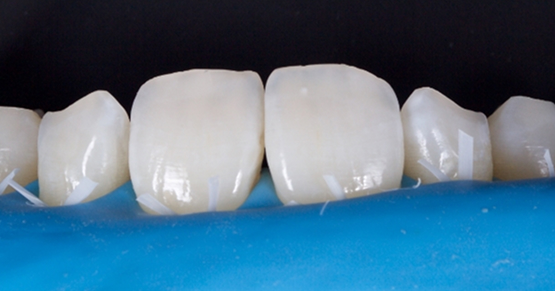
Posterior Full-Contour Zirconia Crowns: Preparation Design
One significant advantage of this restoration is that the preparation can be more conservative than other all-ceramic or even metal-ceramic restorations, with a preparation design similar to that of a full cast gold crown. The amount of space required will vary slightly depending on the detail of occlusal morphology expected in the outcome.
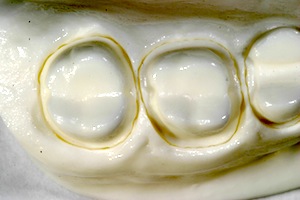
In the above images, you’ll see:
- The first molar is prepared for a full-contour monolithic e.max crown. There is a 1.5–2 mm cusp tip/occlusal reduction. There is a 1 mm circumferential shoulder reduction (round internal line angle), a 6–8° taper to axial walls, and a 1.5 mm occlusal-third reduction of the functional cusp.
- The second molar is prepared for full-contour monolithic zirconia crown. There is a 1–1.5 mm occlusal depth cut to achieve appropriate occlusal anatomy, a 1–1.5 mm functional cusp tip reduction, a 0.5 mm gingival chamfer reduction, a 6–8° taper to the axial walls, and a 1 mm occlusal-third reduction of the functional cusp.
Margin design
- 0.3 to 0.5 mm chamfer
- This allows for a more accurate mill of the presintered zirconia.
- If a knife or feather-edge preparation is established instead of a chamfer, a restoration can be milled but there is a slightly higher risk of chipping the presintered zirconia during the milling process. With this margin design during the CAD procedure, additional contouring to the crown would be done to increase the thickness of the zirconia to minimize the chipping during the CAM phase of production.
- After sintering, the crown contour at the margin can be reduced or thinned using rubber wheels before the characterization and glazing process.
Functional cusp reduction
- It is recommended to reduce the functional cusp 1-1.5 mm.
- This allows for possible changes in crown morphology and possible alteration of the occlusion.
Axial wall reduction
- It should taper 6–8° from the margin to the occlusal third, achieving a depth of 1 mm.
- All transitional edges, angles, and corners must be rounded.
Occlusal reduction
- Central groove should be reduced 1–1.5 mm. This allows space for developing occlusal anatomy.
- The resulting central groove crown thickness may be as thin as 0.5 mm once the anatomy is added, yet there is still adequate strength to the restoration.
- If the occlusal reduction space created is less than 1 mm, the morphology will typically become saucer-shaped and the technician is forced to scratch the surface to provide some sort of anatomy, rather than creating a more natural appearance.
The resulting thickness of the zirconia restoration will impact the masking ability of a discolored underlying prepared tooth. The thinner the zirconia, the more translucent it will be, allowing the underlying tooth substrate to affect the esthetics of the final outcome. Increasing the thickness of the zirconia (increasing the depth of the tooth reduction) will mask the discoloration but will increase the relative opacity of the zirconia because it is a monolithic restoration. It may therefore appear higher in value, or brighter, than adjacent natural teeth or other restorations.
VIRTUAL SEMINARS
The Campus CE Experience
– Online, Anywhere
Spear Virtual Seminars give you versatility to refine your clinical skills following the same lessons that you would at the Spear Campus in Scottsdale — but from anywhere, as a safe online alternative to large-attendance campus events. Ask an advisor how your practice can take advantage of this new CE option.

By: Robert Winter
Date: October 27, 2016
Featured Digest articles
Insights and advice from Spear Faculty and industry experts